Exploring the Mysterious World of Caecilians: Nature’s Enigmatic Amphibians
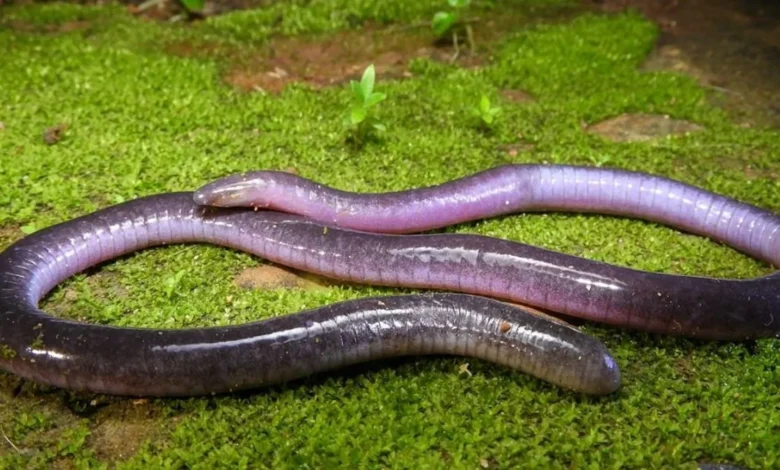

Caecilians are one of nature’s most fascinating and enigmatic creatures, often overlooked due to their secretive, burrowing lifestyles and their uncanny resemblance to worms or snakes. Unlike other amphibians that are well-known and widely studied, such as frogs and salamanders, remain something of a mystery to the scientific world and the public. With their unique adaptations and unusual appearance, represent a branch of the amphibian family tree that still holds many secrets.
In this article, we’ll take an in-depth look at these intriguing animals, exploring everything from their physical characteristics and behaviours to their habitats and role in the ecosystem. Caecilians may be elusive, but they are no less important in their ecosystems than their more famous amphibian relatives. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of and why they are so unique in the animal kingdom.
What Are Caecilians?
Caecilians are a distinct group of limbless amphibians that belong to the order Gymnophiona. They are primarily found in tropical regions, where they spend most of their lives underground or hidden beneath leaf litter and soil. Unlike other amphibians that undergo dramatic transformations during their life cycles, have evolved in a way that allows them to remain relatively hidden and avoid detection by predators.
Physically, caecilians have long, cylindrical bodies covered with smooth, often slimy skin. They can vary in size, ranging from a few inches to several feet, depending on the species. are also characterized by their reduced or absent eyes, which are usually covered by skin or bone. This adaptation makes sense given their burrowing lifestyle, where sight is less important than touch and smell. They use their well-developed sense of smell and specialized tentacle-like organs near their nostrils to navigate their subterranean environments and locate prey.
The Unique Physical Characteristics of Caecilians
Caecilians possess several distinctive physical traits that set them apart from other amphibians. One of the most noticeable features is their segmented appearance, which is created by ring-like folds, or annuli, that run along their bodies. These annuli are often mistaken for segments like those found in earthworms, but they are simply folds in the skin and do not indicate true body segmentation.
In addition to their annuli, caecilians have a specialized jaw structure that allows them to burrow efficiently and capture prey. Unlike other amphibians, have a unique two-part jaw mechanism that enables them to deliver a powerful bite. This adaptation is essential for a lifestyle that requires digging through dense soil and capturing small, elusive prey like earthworms, insects, and other invertebrates. Their teeth are small but sharp, well-suited for gripping and consuming their soft-bodied prey.
Habitat and Distribution of Caecilians
Caecilians are primarily found in tropical regions around the world, with the highest concentrations in South America, Africa, and parts of Southeast Asia. Their habitats range from rainforests to grasslands, but they are almost always found in moist environments where the soil is soft enough for burrowing. Because they spend so much of their lives underground, are rarely seen by humans, contributing to their reputation as one of the least understood groups of amphibians.
The secretive lifestyle of caecilians makes studying them in the wild a challenge. Most are discovered accidentally, often by researchers or locals who happen upon them while digging or during heavy rains when the animals are occasionally forced to the surface. This elusive nature has limited scientific knowledge about their population sizes and the specific environmental factors that affect their distribution. However, play a vital role in their ecosystems, particularly in soil health and nutrient cycling.
Reproduction and Life Cycle of Caecilians
One of the fascinating aspects of caecilians is their reproductive behaviour, which differs significantly from that of other amphibians. Many caecilian species are viviparous, meaning they give birth to live young rather than laying eggs. In viviparous, the developing embryos feed on a nutrient-rich secretion produced by the mother, a phenomenon known as matrotrophy. This process is akin to a primitive form of placental nourishment, which is quite rare in amphibians.
In some oviparous species, the mother lays eggs, and the young hatch into a larval stage before eventually transforming into adults. However, even among egg-laying caecilians, parental care is often observed. Some species have been observed providing nourishment to their young by allowing them to feed on the outer layer of the mother’s skin, which she regenerates specifically for this purpose. This unique form of parental care is rarely seen in the amphibian world and highlights the remarkable adaptations have evolved to ensure the survival of their young.
Diet and Feeding Behavior of Caecilians
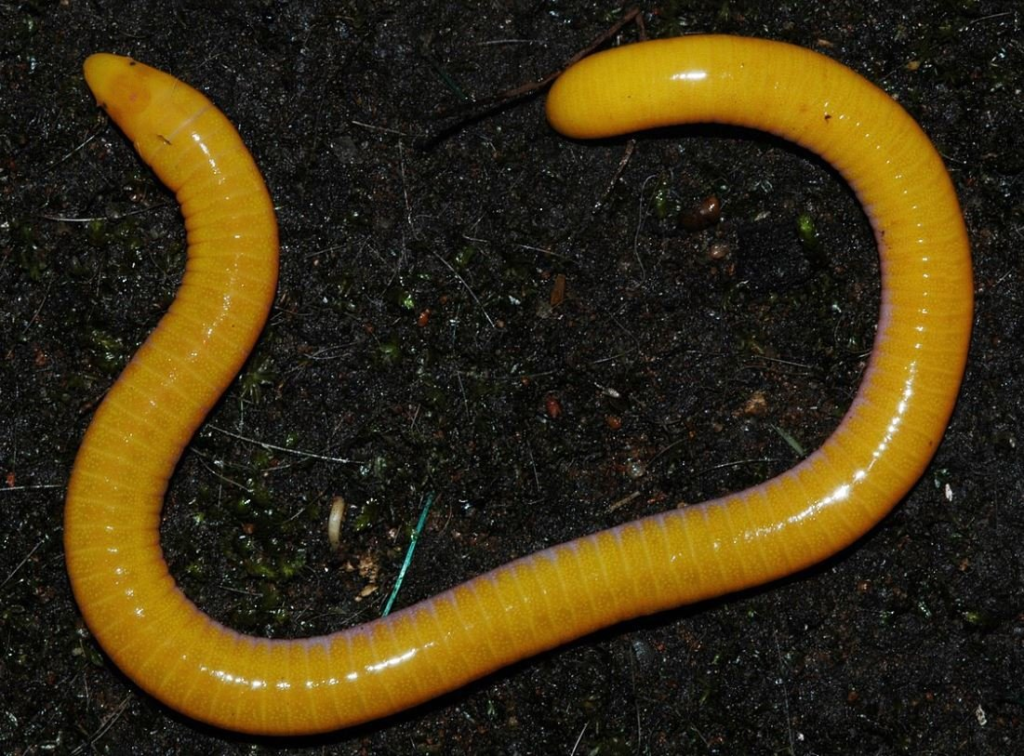

Caecilians are carnivorous and feed primarily on small invertebrates such as earthworms, insects, and other soft-bodied creatures. Their diet is highly adapted to their subterranean lifestyle, as they rely on their keen sense of smell and specialized jaw structure to locate and capture prey in the dark. In the soil, where vision is practically useless, have evolved to use chemosensory tentacles located near their nostrils to “taste” or “smell” their surroundings, helping them detect prey even when it is buried.
The feeding mechanism of caecilians is also unique among amphibians. They use a powerful bite to capture and consume their prey, and their jaws are structured to open wide, enabling them to swallow prey whole. This adaptation is essential for, as their diet consists mostly of soft-bodied animals that are easier to digest. Their feeding behaviour has a positive impact on the soil ecosystem, as help control populations of soil-dwelling invertebrates and contribute to nutrient cycling.
The Role of Caecilians in the Ecosystem
Although they are often overlooked, caecilians play a crucial role in the ecosystems they inhabit. As burrowers, help aerate the soil, which can improve water infiltration and root growth for plants. Their feeding habits also help control populations of soil-dwelling invertebrates, creating a balanced ecosystem below the surface. By breaking down organic material and aiding in nutrient cycling, indirectly contribute to the health and productivity of plant life in their habitats.
Additionally, caecilians serve as prey for various predators, including snakes, birds, and mammals, contributing to the food web in tropical ecosystems. Their presence, although often unseen, is an important part of the complex network of interactions that support biodiversity. Caecilians may not be as visible as other animals, but their ecological role is just as vital for maintaining the health of their environments.
Challenges and Threats Facing Caecilian Populations
Caecilian populations are facing numerous challenges, many of which are linked to human activities. Habitat destruction, particularly deforestation in tropical regions, poses a significant threat to caecilian populations. As forests are cleared for agriculture or urban development, caecilians lose the moist, sheltered environments they rely on for survival. The reduction of their natural habitat limits their ability to find food, reproduce, and avoid predators, putting their populations at risk.
In addition to habitat loss, pollution and climate change also threaten caecilian populations. Chemical pollutants in soil and water can disrupt their delicate skin and respiratory systems, while changes in temperature and rainfall patterns can make their habitats less hospitable. Climate change, in particular, poses a long-term threat to caecilian populations, as shifts in weather patterns can lead to drier conditions that are unsuitable for their burrowing lifestyle.
Conservation Efforts for Caecilians
Despite the threats facing caecilian populations, conservation efforts aimed at protecting these unique animals are still in their early stages. Because caecilians are so elusive and difficult to study, they have not received the same level of attention as other amphibians in conservation programs. However, as scientists learn more about and their ecological importance, efforts to protect their habitats and populations are slowly gaining momentum.
Conservation strategies for caecilians typically focus on preserving their natural habitats, particularly tropical forests where the majority of caecilian species are found. Protecting these habitats from deforestation and pollution is essential for ensuring the survival of caecilian populations. Additionally, raising awareness about the importance of caecilians in the ecosystem can help generate public support for conservation initiatives aimed at protecting these little-known amphibians.
The Importance of Studying Caecilians
Studying caecilians is essential for understanding the full diversity of life on Earth and the complex ecosystems that sustain it. As one of the most unique and least understood groups of amphibians, caecilians offer valuable insights into evolutionary biology, ecology, and animal behaviour. By studying caecilians, scientists can learn more about the adaptations that allow animals to thrive in specialized environments, as well as the evolutionary history that has shaped the diversity of life on our planet.
In addition to their scientific value, caecilians may also have potential applications in fields like medicine and biotechnology. For example, their skin contains various compounds that may have antibacterial or antifungal properties, which could be valuable in developing new treatments. Studying caecilians could reveal other unexpected benefits, underscoring the importance of conserving these animals and their habitats.
The Future of Caecilians: Challenges and Opportunities
The future of caecilian populations will depend on a combination of conservation efforts, scientific research, and public awareness. As more people become aware of the ecological importance of caecilians, there is hope that conservation initiatives will gain more support. Continued research is essential for understanding the specific needs of different caecilian species and for developing effective conservation strategies.
The opportunities for studying caecilians are vast, and as technology advances, scientists may be able to uncover